Liver Blood Test Pathway
Pathway
Pathway Algorithm
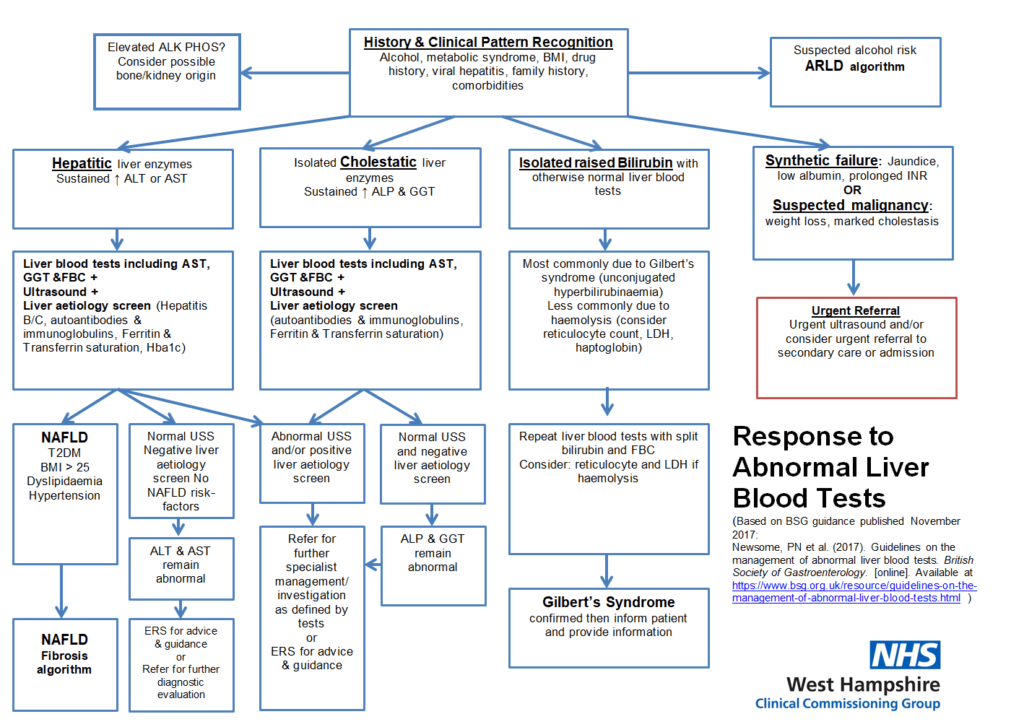
- Liver Disease is under diagnosed;
- It’s increasing and the 3rd most common cause of premature death;
- Traditional LFT’s do not measure Liver Function;
- Abnormal LFTs do need investigating;
- Normal LFTs DO NOT exclude advanced liver disease – BE SUSPICIOUS
- Most patients are asymptomatic until the end stages. “All roads (causes) lead to cirrhosis”
- INTERVENE: 90% is preventable (long lead time – 10yrs) but most patients are asymptomatic. (Commonest causes are ALL preventable – NAFLD (now the most common), alcohol (with the worst disease trajectory) and viral.
- To help the clinician to identify at risk patients (ALCOHOL, FAT, VIRAL), prevent disease, allow earlier diagnosis/staging Liver conditions and make targeted interventions to reduce disease burden and lost early adult life years.
- To improve patient outcomes through education, understanding and self-management and through behavioral/lifestyle advice and treatment/follow up where appropriate.
- REFER as per Pathway:
- Emergency/D/w duty if synthetic failure or > 10xNormal
- TWR according to Guidelines
- Repeat Bloods within few days if >5x normal or weeks if <5xNormal, with further Liver Screen/CVS Bloods and appropriately timed USS.
- eRS advice/guidance or refer onwards Urgent/Routine
- Record alcohol
- Screen at risk
- Routine and opportunistic checks and if relevant conditions
- AUDIT-C. If drinking more than recommended:
- Code/register of those identified as XS intake/heavy or dependent, brief intervention, refer/decline in depth alcohol/lifestyle support, further lx as appropriate pathway. RECALL!
- Identify those at risk of chronic viral B/C
- Search / Identify (e.g. IVDU, Transfusion, Occupation, and Ethnicity/Travel).
- Test – IMMUNISE / Refer.
- HEP B:
- Immunise those at risk of transmission e.g. CLD, CKD, Contacts, IVDU, Travel, frequent partner change.
- HB+ve: annual flu vaccination, check Hep A immunity, reduce other RF e.g. weight/ETOH.
- NAFLD
- CODE high BMI, Brief intervention, Refer/decline exercise/diet? BARIATRIC, consider Risk.
- CHILD Liver Disease/Obesity.
- Liver diseases e.g. PBC, Hemochromatosis
Extra considerations
- Remember other causes of raised ALT e.g. non-hepatic: thyroid, MSK, coeliac.
- ALT <3x Normal and normal Ix Liver screen: no action needed – monitor.
- Raised ALP and normal GGT: consider Vit D/Bone/Pregnancy (N.B. 3rd Trimester associated with poor prognosis)
- Raised ALP <2x normal and normal Ix: Incidental.
- Raised ALP and GGT <100 and other Ix normal: Incidental.
This includes advice on management of liver conditions.
